International commissions and organizations have created standards that can be applied to data controllers who do business across borders, especially those who are required to follow GDPR.
One well-known option is provided by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), specifically ISO/IEC 27001, recently amended in 2019 with the ISO/IEC 27701 document.
Lesser-known in the U.S., but possibly more relevant to businesses that work between borders and certainly more unique in its controls, is the Cross Border Privacy Rules (CBPR) framework, provided by the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC). Both ISO/IEC 27701 and APEC CBPR are voluntary, available in the US, and internationally relevant; also, both at least somewhat overlap with GDPR requirements.
ISO/IEC 27701: 2019
The ISO/IEC 27701 standard provides requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS) for data controllers, processors, and intermediaries.
It provides data extension to 2013’s ISO/IEC 27001 and 27002 security controls to take into account some additional requirements, like information security, and the protection of individual consumers’ privacy. It is meant to map some provisions against GDPR, amongst other requirements.
The certification requires renewal every three years and is assessed by either internal or external auditors who are accredited against the ISO conformity assessment.
What is the Process of Achieving an ISO/IEC 27701 Certification?
Gap Analysis. This pre-assessment compares the Privacy Information Management System (PIMS) with ISO/IEC 27701’s requirements.
Readiness Review. This is the Stage 1 audit, where the assessor conducts a review of the organization’s preparedness for further assessment by checking if the proper controls have been developed. Sometimes this is referred to as a tabletop audit and is used to verify the design of controls.
Formal Audit. This is the Stage 2 audit, where, if all requirements are in place, the assessor reviews the implementation of procedures. During this stage the auditor performs testing of the control effectiveness by developing test plans, performing testing and analyzing evidence. The goal is to determine if the PIMS is operating as designed.
What Are ISO/IEC 27701’s 14 Controls?
The more general ISO/IEC 27001, upon which ISO/IEC 27701 is based, contains 14 control categories, and a total of 133 controls.
The 14 categories are:
- Information Security Policies
- Organization of Information Security
- Human Resource Security
- Asset Management
- Access Control
- Cryptography
- Physical and Environmental Security
- Operations Security
- Communications Security
- System Acquisition, Development, and Maintenance
- Supplier Relationships
- Information Security Incident Management
- Information security aspects of business continuity management
- Compliance
How Much Does Achieving ISO/IEC 27701 Certification Cost?
The short answer is the costs include the accredited certification body’s fees and the cost of the standard document.
Copies of the standard cost $120 or more per copy, but expenses for achieving certification can include a course that quality team members or others need internally or fees associated with the application, intake, and processes through external auditors. It can get expensive quickly. One study from 2012 cited an average reported cost of around $48,000, but with normal inflation, that would be just over $53,000 today.
How Does ISO/IEC 27701 Measure Against GDPR?
ISO/IEC 27701 is an addition to 27001, which is a somewhat generic standard, focusing on the security management systems needing to be in place to support the protection of information. While it can be helpful in the operational implementation of dealing with GDPR articles 32 and 25 of GDPR, it lacks coverage in other areas.
ISO/IEC 27701 addresses some of these gaps but does not address the oversight and accountability element in Article 42 of GDPR.
The APEC CBPR
The APEC Cross-Border Privacy Rules (CBPR) System, endorsed by the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation in 2004, is a voluntary, enforceable, international, accountability-based system that facilitates privacy-respecting data flows among APEC economies. APEC CBPR provides a standard set of principles designed to enhance electronic performance, facilitate trade and economic growth, and strengthen consumer privacy protections.
What’s unique about APEC CBPR is that, while it is entirely voluntary, it also has an element of independent accountability oversight, complaint mitigation, and legal enforceability, making it the strongest candidate for demonstrating a commitment to privacy.
Commonly misconceived as a solely Asian-Pacific-based system, CBPR is active between the USA, Mexico, Japan, Canada, Singapore, the Republic of Korea, Australia, Chinese Taipei, and the Philippines, with more expected to join soon.
What Makes CBPR Legally Enforceable?
A central element of CBPR is it is legally enforceable in each of the APEC economies. Within the U.S., CBPR certification processes work in coordination with and under the enforcement authority of the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The FTC enforces Section 5(a) (15 USC§45), which enforces “unfair or deceptive acts or practices in or affecting commerce.” The failure of organizations to abide by their own privacy policies can be enforced by the FTC under their Section 5 authority.
Accountability Agents: APEC’s Line of Defense Against Internal Abuse
CBPR’s Accountability provisions go above and beyond to ensure voluntary and continued accountability by instating recognized Accountability Agents (akin to assessors or auditors under other standards) instead of allowing internal or independent auditing. Accreditation by APEC to issue certifications requires rigorous review and acceptance by the Joint Oversight Panel. Recognition as an Accountability Agent must be re-applied every two years. This is not the case with third-party ISO auditors. Currently, there are only four Accountability Agents in the US (one of which is NCC Group) and a total of eight globally.
Accountability agents are responsible for reviewing CBPR applicants, recommending changes, and in many cases, helping them develop data privacy protocols before issuing the certification.
Accountability Agents must be able to demonstrate the following:
- The processes in place to ensure its independence
- The organization of the certification process
- The monitoring and compliance review processes
- The renewal process
- The dispute resolution process
- The mechanisms in place for enforcing the CBPR program requirements
Most notably, Accountability Agents also provide continued oversight of certified business practices for one calendar year. Because CBPR-certified companies are added to a public directory on the APEC website, anyone with concerns or complaints can find a listing and report violations of data privacy policy--this would then prompt the certifying Accountability Agent to launch an investigation and address the issue between both parties.
In other words, having a CBPR certification on a business’ website and materials implies that:
1. They have gone through rigorous assessments and created data control processes that meet high standards;
2. That they are committed to following their data policies with the possibility of legal ramifications should they fail;
3. They are committed to full transparency regarding how they handle personal data--they won’t misuse or abuse it.
What Are APEC CBPR’s Controls?
APEC CBPR has 50 flexible but ethically precise controls that fall under 9 privacy principles:
- Accountability
- Preventing Harm
- Notice
- Choice
- Collection Limitations
- Use of Personal Information
- Integrity of Personal Information
- Security Safeguards
- Access and Correction
Unlike ISO/IEC 27701, all self-assessments and controls are transparent, free to access, and readily available online at their website. For more information, visit their documents page.
What’s the Process of Achieving an APEC CBPR Certification?
- The Accountability Agent performs an initial assessment based on the applicant’s self-evaluation and intake.
- The Accountability Agent then provides a comprehensive report to the applicant’s outlining findings regarding compliance requirements.
- The Accountability Agent verifies that any required changes, as outlined in the findings report, have been adequately implemented.
- Upon successful conclusion of the above steps, the Accountability Agent certifies that the applicant complies with their program requirements.
- The agent posts a CBPR-certified company on the APEC CBPR directory, and the applicant can use CBPR-related seals and add it to their materials.
How Much Does Achieving APEC CBPR Certification Cost?
According to APEC, costs are to be kept minimal under this standard to allow widespread use and a low financial bar to entry. The cost to certify is similar to the cost of a compliance assessment of HIPAA or PCI.
How Does APEC CBPR Measure Against GDPR?
According to a 2019 study conducted by the European Commission on Data Protection Certification Mechanisms, “Certification schemes focusing on international data transfer remains rare. CBPR offers an interesting and valuable insight into cross-border data flows and its certification.”
APEC CBPR was deemed likely to offer modules for the GDPR data protection certification as a means of transfer. The scheme arrangement of the standard is very similar to the mechanism suggested in Article 42 of GDPR, where authorities are entitled to draft requirements and then accredit private certification bodies to manage the scheme under their monitoring.
The choice made by the CBPR board to renew the certification and accreditation process every two years directly demonstrates a desire to address this very concern, ensuring close monitoring of both accountability agents and certified organizations.
How do ISO/IEC 27701 and APEC CBPR Compare?
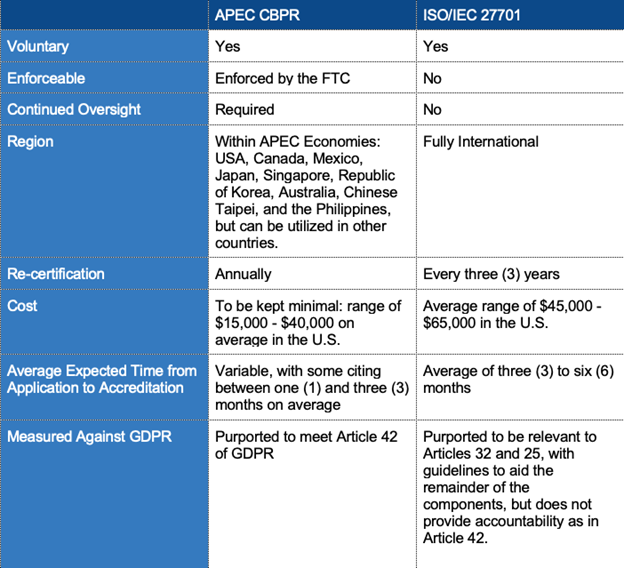
Where can I get more information on ISO/IEC 27701 and APEC CBPR?
NCC Group helps companies conduct ISO/IEC 27701 gap assessments and pre-audits, In addition, NCC Group is one of only four APEC-Recognized Accountability Agents in the United States (and one of eight globally) authorized to perform a CBPR certification on U.S. organizations.
Reach out to one of our international compliance specialists to see if APEC CBPR is the right fit for you.